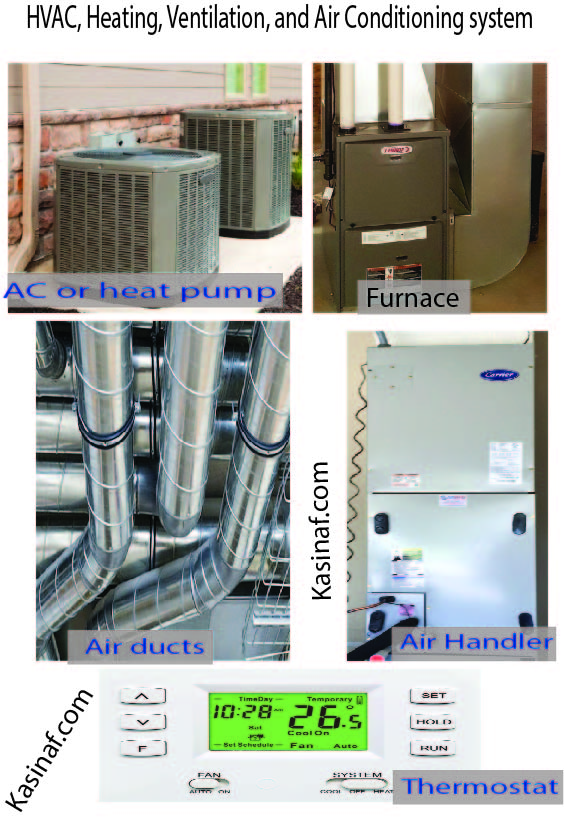
Evap. coil is a short form of Evaporator coil
An air conditioning system or HVAC system has two coils, these include the evaporator coil and condenser coil. The two coils makeup the air conditioning unit coils,
these air conditioning coils are explained in this article
In the scorching heat of summer, your knowledge about your air conditioner might cover the basics, but have you ever wondered about the inner workings of the coil for ac (evaporator and condenser coils)? If the technical side of your AC remains a mystery, understanding a few key details about how it cools your home can be beneficial.
Regardless of how often your air conditioning unit runs, regular maintenance is crucial to keep your air conditioning unit coils operating effiecntly, along with the entire system, working efficiently. This becomes especially important when something goes wrong, as having a basic understanding allows you to troubleshoot issues and make informed decisions about replacements or upgrades.
Imagine a malfunctioning AC that refuses to turn on or worse, blows warm air in the midst of a hot summer day. To avoid this, it’s vital, with the assistance of a professional HVAC technician, to ensure your air conditioner’s evap coils is in optimal condition. These A C coils play a significant role as it absorbs heat from inside your home and collaborates with other AC components to cool your space by moving that absorbed heat outside. If the evaporator coil malfunctions, your home won’t cool as desired, making it crucial to understand how air conditioning coils work and how to maintain it to prevent AC breakdowns in the summer.
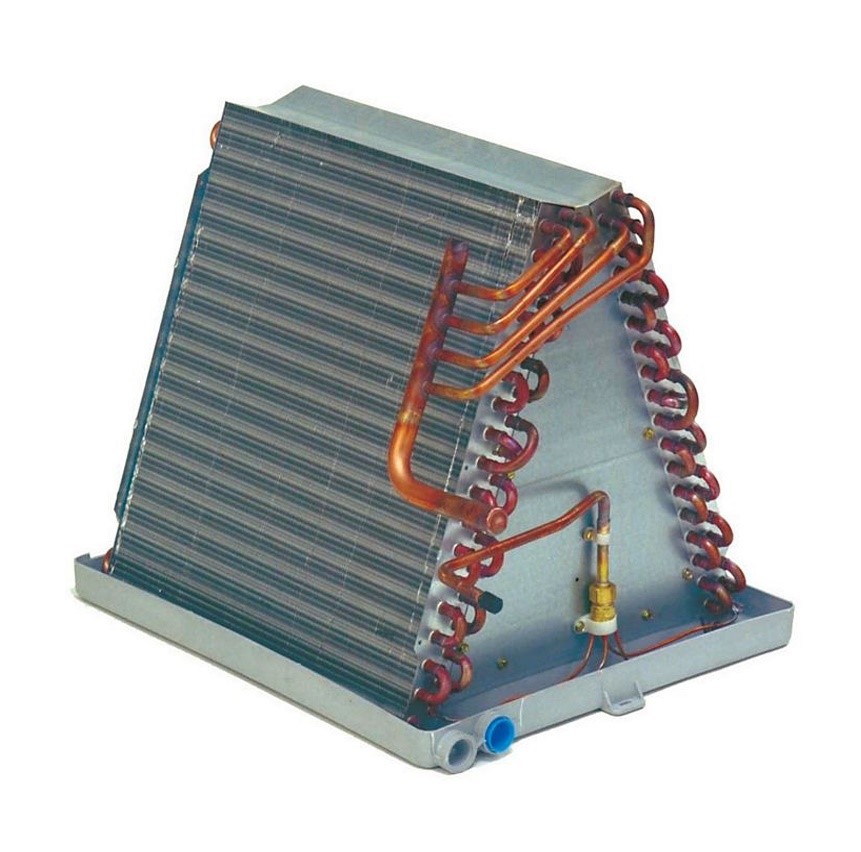

Understanding AC evaporator coil
An evaporator coil is the component of air conditioner or heat pump that absorbs the heat and moisture from the air inside your house. It works alongside the condenser coil to produce cool air and complete the heat exchange cycle.
Air conditioners don’t produce cold air like a furnace generates heat. Instead, they use a substance called refrigerant to absorb heat from the air inside your home. This heat is then carried outside and released into the outdoor air.
The refrigerant keeps moving, repeating this process until your indoor air reaches the temperature you set on the thermostat.
Now, let’s focus on the evaporator coil. It’s a crucial part of your air conditioner, working to absorb heat and moisture from the indoor air. The evaporator coil collaborates with the condenser coil to create cool air, completing the cycle of heat exchange.
A quick note: Be cautious! Air conditioners have high-voltage parts, and handling them without expertise can be dangerous. If you’re having issues, always consult a licensed HVAC technician for assistance. They have the knowledge to keep you safe and your air conditioner running smoothly.
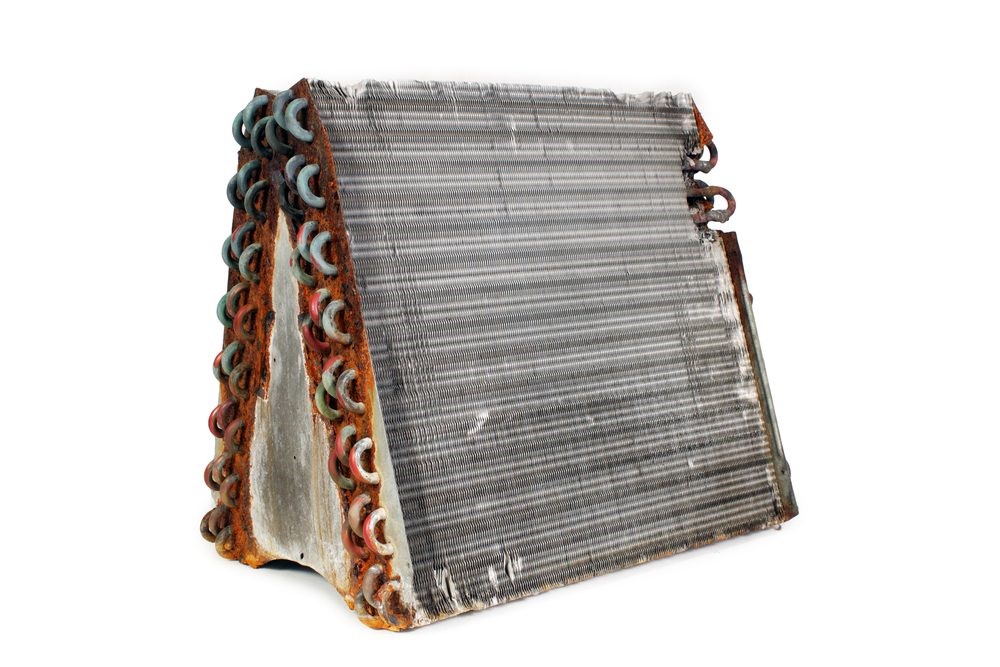

How AC evaporator coil works
An air conditioner’s evaporator coil (evap coil), it is also called evaporator core, is a vital part responsible for making the air cold by using the refrigerant to absorb heat.
This AC coil is located inside your house near the blower fan in the air handler. These air conditioning unit coils are typically made from materials like copper, steel, or aluminum because they are good at conducting heat. In most home AC systems, the evaporator consists of U-shaped tubes set into panels arranged like an “A.” These panels have fins that help bring warm air closer to the coils, maximizing the cooling effect of the refrigerant.
When AC runs, the compressor pulls cold, low-pressure liquid refrigerant through the tubing in the evaporator coil. Before entering the evaporator coil, the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve. This valve relieves pressure from the liquid refrigerant, which rapidly cools it. The liquid refrigerant leaving the expansion valve is quite cold, which allows it to absorb heat from the air.
The expansion valve also controls how much refrigerant flows to the evaporator. More advanced expansion valves, such as thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs), can precisely control the flow to improve the system’s overall energy efficiency.
As the refrigerant flows, the blower fan draws hot room air over the evaporator coil. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the passing air, and as it does so, it warms up and evaporates.
When the water vapor in your warm household air hits the cold evaporator coils, the water vapor condenses into liquid and drips down into the condensate pan, which drains the water away outdoors. This is how your evaporator coil reduces the humidity in your home.
Essential Care for Your Evaporator Coil
Role of Evaporator Coils Evaporator coils are vital components in air conditioning systems, responsible for cooling the air by absorbing heat. Alongside condenser coils, they play a crucial role in maintaining optimal energy efficiency. However, the efficiency and functionality of evaporator coils can be compromised if they’re not properly maintained.
Effects of a Dirty Evaporator Coil on Your HVAC System
Effects of poorly maintained evaporator coil
Your home’s HVAC system consists of various components working together to keep you comfortable. Among these, the evaporator coil plays a crucial role in cooling your indoor air. However, when this component becomes dirty, its effects can extend beyond just reduced efficiency.
Reduced ability to absorb heat and cool effectively. The primary function of the evaporator coil is to absorb heat from the air, allowing it to cool before circulating it back into your home. When the coil is covered in dirt or dust, its ability to absorb heat is significantly impaired. This results in a reduced cooling capacity, making it harder for your HVAC system to maintain the desired indoor temperature.
Higher Energy consumption. A dirty evaporator coil forces your HVAC system to work harder to compensate for its reduced efficiency. As the coil struggles to absorb heat efficiently, the system runs for longer cycles, consuming more energy to achieve the same level of cooling. This increased energy consumption reflects in higher utility bills.
Higher Pressures and Temperatures The accumulation of dirt and debris on the evaporator coil obstructs the heat transfer process. As a consequence, the system experiences higher pressures and temperatures as it attempts to compensate for the reduced heat absorption. This added strain on the system can lead to wear and tear on other components, potentially resulting in costly repairs.
Frost and Ice Buildup One of the most visible effects of a dirty evaporator coil is the development of frost or ice. When the coil fails to absorb heat efficiently, the refrigerant within doesn’t warm up as required. This causes moisture in the air to freeze on the coil’s surface, leading to frost or ice buildup. If left unchecked, this buildup can further decrease the coil’s effectiveness and damage other system components.
Regular maintenance of your HVAC system, including the cleaning of the evaporator coil, is essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. By addressing the effects of a dirty coil—such as reduced cooling capacity, increased energy consumption, elevated pressures and temperatures, and frost buildup—you not only maintain a comfortable indoor environment but also extend the lifespan of your HVAC system while keeping utility costs in check. Prioritizing the cleanliness of the evaporator coil can go a long way in ensuring your system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Top of Form
More information about air conditioner evaporator coil
The Impact of Dust and Debris
Even a thin layer of dust on the evaporator coil can significantly hinder its performance. Dust acts as an insulator, preventing efficient heat absorption and disrupting the cooling process. This inefficiency leads to increased energy consumption as the system works harder to achieve the desired indoor temperature.
A dirty evaporator coil can result in various issues, including higher pressures, temperatures, and frost or ice buildup. When the coil fails to absorb sufficient heat due to dirt accumulation, the refrigerant within doesn’t warm up as needed. This cold refrigerant causes moisture in the air to freeze on the coil’s surface, leading to frost accumulation. Allowing the system to operate with a frozen evaporator can eventually damage the compressor, risking system failure.
Identifying Problems and Seeking Help
Multiple factors, such as dust accumulation, debris in the condenser unit, clogged air filters, or refrigerant leaks, can cause evaporator coils to freeze. If you’re unable to pinpoint the issue, seeking assistance from a heating and cooling technician is crucial to prevent further damage.
Understanding Coil Leaks and Prevention
In addition to dirt accumulation, evaporator coils can develop tiny leaks due to corrosion caused by the mixture of moisture and household chemicals. Signs of leakage include oily residue around the coil or in the drain pan. This issue requires immediate attention and may necessitate coil replacement to prevent further damage.
Protecting Your Coil and Health
Chemicals known as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from various household sources contribute to coil corrosion. Proper home ventilation is essential to reduce VOC levels indoors, safeguarding both the evaporator coil’s integrity and your health.
Regular maintenance and attention to your evaporator coil are essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency in your air conditioning system. By addressing dust accumulation, potential leaks, and controlling indoor air quality, you not only protect your coil but also contribute to a healthier living environment. Remember, seeking professional help when needed can prevent major issues and extend the life of your cooling system.
Condenser coil
The evaporator coil and condenser coil team up to make your home cool. The evaporator coil can’t do its job properly without the condenser coil finishing the cooling process. They work together like a pair to make sure your home stays nice and cool.
The evaporator coil performs the first half of the cooling cycle and the condenser coil performs the second half of the cooling cycle.
Your air conditioner’s condenser is located in the large exterior unit, plays a crucial role in the cooling process. Often referred to as the “condenser unit,” it comprises various components, including condenser tubes, fins, a compressor, a fan, copper tubing, valves, and switches, all working together to facilitate the cooling mechanism.
What is an AC Condenser?
The condenser serves as a vital part of your air conditioning system, responsible for transforming refrigerant from a gas to a liquid state. Housed in the outdoor unit, it collaborates with other components to efficiently manage heat transfer.
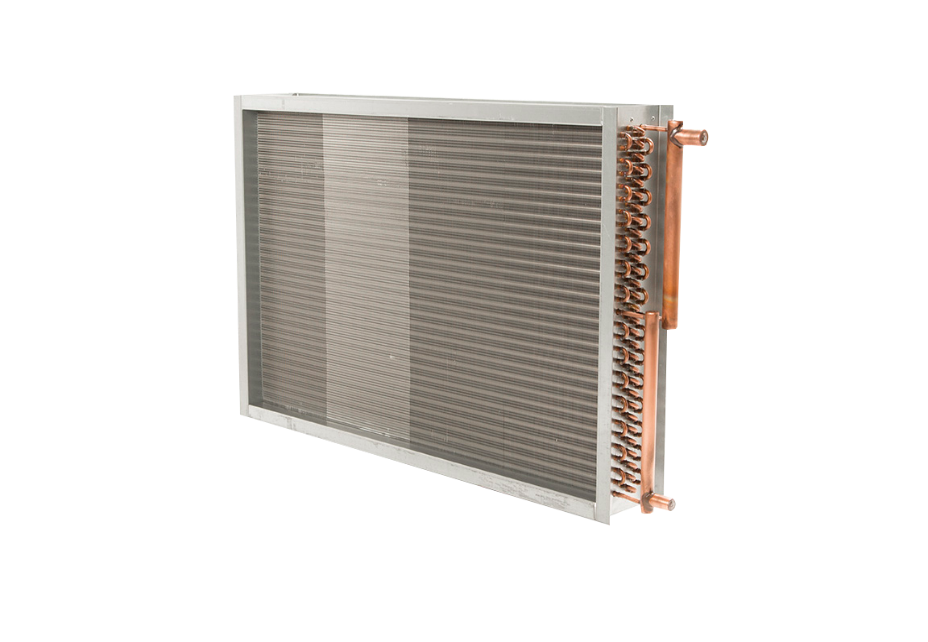

The Working Mechanism of operation of AC condenser coil:
- Refrigerant Journey: After absorbing heat from your home’s air, the refrigerant travels through a copper tube to reach the condenser unit. At this stage, it exists as a low-pressure, warm gas.
- Compression Process: Upon entering the compressor within the condenser unit, the refrigerant undergoes pressurization, converting into a hot, high-pressure gas. This step is critical in preparing the refrigerant for the subsequent cooling process.
- Heat Release in Condenser Coils: The high-pressure gas moves into the condenser coils, where it sheds much of the heat absorbed from your home. The fan atop the outdoor unit assists by blowing air over these coils, aiding the refrigerant in losing heat. The numerous coils in the condenser prolong the contact between the refrigerant and the blowing air, allowing for efficient heat dissipation.
- Transition to Liquid State: As the refrigerant releases heat, it changes from a hot gas to a hot liquid. This transition occurs within the condenser, marking a crucial stage in the cooling cycle.
- Return to the Indoor Unit: The now-cooled liquid refrigerant flows back through copper tubing into your home, making its way to the expansion valve located near the evaporator coil, situated in the indoor unit.
Conclusion: The condenser unit in your air conditioner is a fundamental component that facilitates the transformation of refrigerant, enabling efficient heat exchange and maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. Understanding how it operates allows for a better grasp of your cooling system’s functionality and the role each part plays in the cooling cycle.
Maintaining Your AC Condenser for Optimal Performance
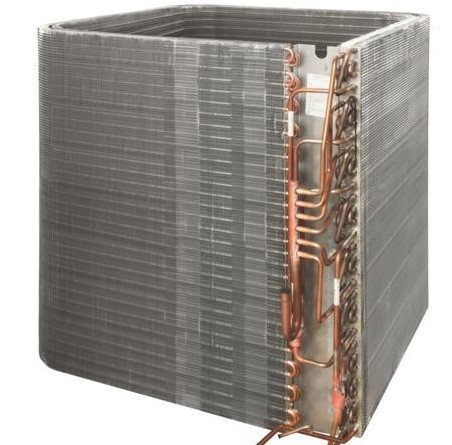

Ensuring the proper functioning of your air conditioner’s condenser is vital for the overall efficiency of your cooling system. This article explores practical steps to keep the condenser in top shape, emphasizing the significance of good airflow for both evaporator and condenser coils.
- Clearing Debris for Uninterrupted Airflow:
One of the primary threats to condenser units is the accumulation of yard debris, such as grass clippings, leaves, twigs, and pet hair, on the fins. This buildup hinders the condenser’s ability to release heat, compromising energy efficiency and putting strain on various components. Regularly check the condenser, and if debris is observed, power off the system and gently clean the fins with a stiff brush to maintain optimal airflow.
- Addressing Ice-ups and Frost:
Occasionally, an AC condenser may develop frost or ice, signaling an airflow issue elsewhere in the system. This could stem from a dirty air filter, clogged air registers and vents, a duct blockage, or a dirty evaporator coil. Low refrigerant levels may also contribute to condenser icing, requiring professional intervention. If ice is detected, it’s essential to investigate and address the root cause to prevent further complications.
- End-of-Season Protection:
As the cooling season concludes, safeguard the outdoor condenser from the elements by covering the top with a piece of wood secured at all four corners by bricks. This precautionary measure prevents snow buildup inside the unit.
- Avoiding Harmful Winter Covers:
While it may be tempting to wrap the condenser in plastic for winter, this approach can have adverse effects. Complete unit covering traps moisture inside, promoting rust, and makes the unit more appealing to animals seeking shelter. A safer alternative is using a piece of wood to cover the top, offering protection without compromising the condenser’s integrity.
Conclusion: Proactively caring for your AC condenser ensures optimal performance and longevity of your cooling system. Regular checks, debris removal, addressing ice-ups, and implementing protective measures at the end of the season contribute to a well-maintained condenser, enhancing the overall efficiency of your air conditioning unit.