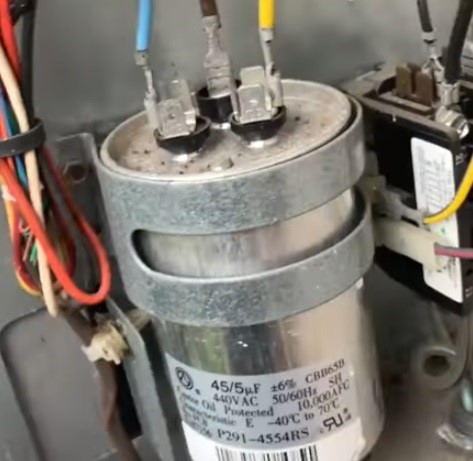
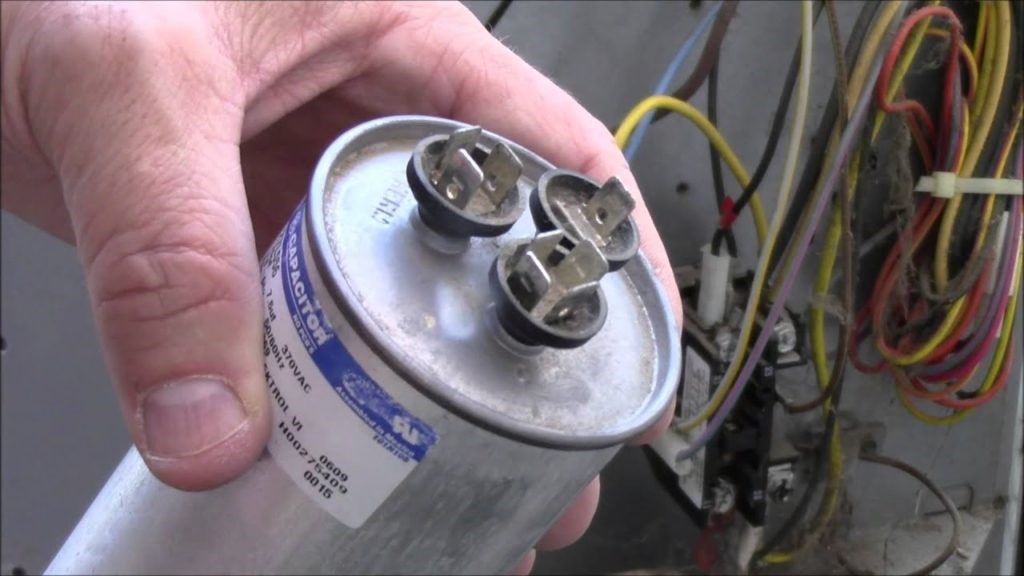
Start and run capacitors are widely used in single phase electric motors for HVAC systems or air conditioning systems (ac), appliances, refrigeration, industrial machinery, and agricultural equipment. They aid motor starting and performance in a range of applications.
To understand capacitors, think of them as similar to batteries, as both store and release electricity. However, capacitors have a distinct function within electrical systems. They store electrical energy and release it at a frequency of 60 times per second in a 60 Hertz system and 50 times per second in a 50HZ ac system.
The size, or capacitance, of a capacitor is crucial for the efficiency of electrical motors, much like the importance of using the right-sized battery in a radio. Just as a radio designed for a 6V battery won’t function properly with a 1.5V battery, a motor that requires a 8 microfarad (uF) capacitor won’t work effectively with a 3.0 uF capacitor. In both cases, mismatched components lead to poor performance.
However, it’s not a case of “bigger is better” when it comes to capacitors. Using an excessively large capacitor can increase energy consumption and cause overheating of motor windings. This, in turn, can shorten the lifespan of the motor.
Motor manufacturers invest significant time in testing different motor and capacitor combinations to identify the most efficient pairing. Replacement start capacitors can have a tolerance of up to +10% in their microfarad rating, but for run capacitors, the replacement must be an exact match. The voltage rating of the replacement capacitor should always be the same as or greater than the original capacitor, whether it’s a start or run capacitor.
It’s advisable to consult with manufacturers or experts to ensure you select the correct capacitor size for your specific application, as the right capacitor is critical for the proper functioning and longevity of motors and electrical systems.
Types of capacitors
Starting capacitors
Starting capacitors are rated in uF range rather than a specific uF rating found on run capacitors. These capacitors, typically rated higher than run capacitors, come in three voltage classifications: 125V, 250V, and 330V. For instance, you might encounter a 35 uF run capacitor at 370V and an 88–108 uF start capacitor at 250V. Start capacitor contains a higher capacitance than a run capacitor.
A start capacitor is found in the circuit of start windings when the motor is starting.
Start capacitors purpose, they enhance motor starting torque, by providing an immediate electrical push to get the motor rotation started. Making it possible to cycle the motor on and off quickly. However, they are meant for momentary use. They remain activated long enough to swiftly accelerate the motor to about 3/4 of its full speed before being removed from the circuit. In essence, start capacitors play a key role in swiftly initiating the motor’s operation.
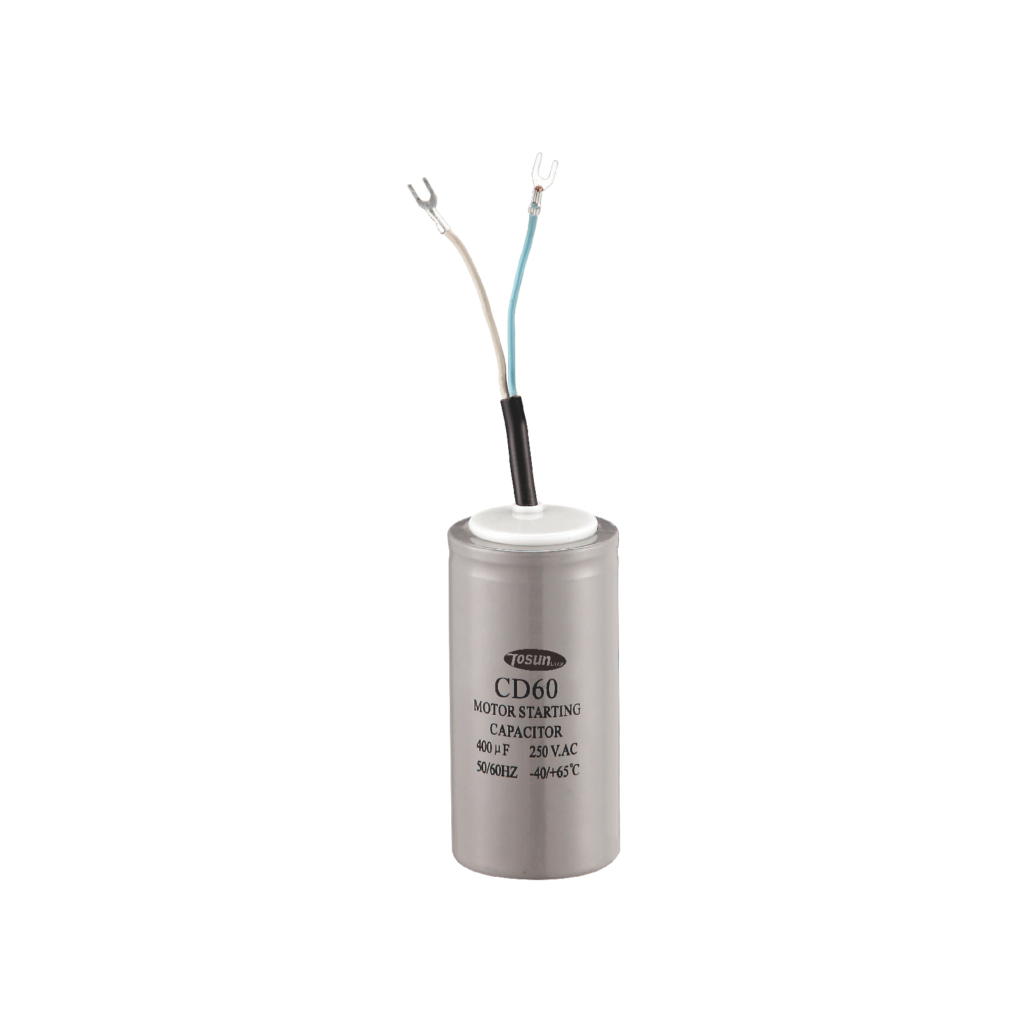

Without a start capacitor when the voltage is applied, the motor would just hum. The start capacitor creates a current to voltage lag in the separate start windings of the motor. The current builds up slowly, and the armature has an opportunity to begin rotating with the field of current.
Run Capacitors:

Run capacitors are crucial components in single-phase electric motors, such as those found in HVAC systems. These capacitors are rated based on their capacitance, typically falling within the range of 3 to 70 microfarads (uF). Usually Capacitors with ratings above 70 microfarad (uF) are starting capacitors. In addition to their capacitance rating, run capacitors are also categorized by their voltage classification, which commonly includes 370V and 440V.
Run capacitors provide constant electrical support during a motor’s operation, they crucial for single-phase electric motors that require them to energize a second winding. Proper sizing is vital because an incorrectly sized run capacitor disrupts the motor’s magnetic field.
For a run capacitor, if capacitance is too high , the phase shift is less than ideal, and winding current becomes too high. Conversely, if the capacitor value is too low, the phase shift increases, resulting in winding current that’s too low. The right balance is crucial for proper motor performance. This irregular field makes the rotor hesitate at uneven points, resulting in noise, higher energy use, reduced performance, and a risk of motor overheating. In essence, choosing the right run capacitor is essential for a smoothly operating motor and system.

why is a run capacitor required to energize the second motor winding?
A run capacitor is required to energize the second motor winding in certain single-phase electric motors to provide the necessary phase shift, which is crucial for the motor’s efficient operation.
Single-phase electric motors have just one power source. Unlike three-phase motors, they lack the balanced power that three-phase motors enjoy. This means they require additional assistance to create a rotating magnetic field necessary for the motor to start and run.
A run capacitor in a single-phase motor energizes the second motor winding by creating a phase shift in the electrical supply, enabling the motor to produce a rotating magnetic field and operate efficiently. This is particularly important for the reliable and robust performance of single-phase motors in various applications.