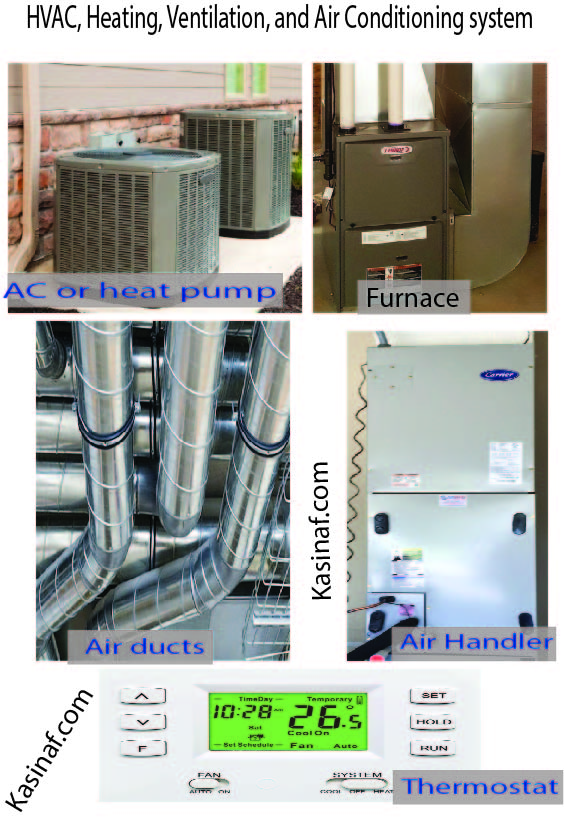
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems play a vital role in creating comfortable and healthy indoor environments. They are integral to maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and air quality in residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the working principles of HVAC systems and their significance in enhancing indoor comfort and air quality.

The General Working Principle of HVAC Systems
HVAC systems work on a basic yet highly effective principle that involves several key components working in tandem. Let’s delve into the intricate details of how HVAC systems operate.
Air Return and Ventilation
The HVAC cycle commences when the air return setup is activated. This setup serves as the entry and exit point for a continuous ventilation cycle. Outside air is drawn into the building through industrial axial fans, while indoor air is expelled through exhaust fans. This constant exchange of air is essential for maintaining fresh indoor air.
Air Filtration
As the air is drawn in, it passes through air filters designed to remove dust and airborne contaminants, including bacteria. This process improves indoor air quality by ensuring that the air entering the building is free from particulate matter.
Temperature Control
HVAC systems provide two primary functions for temperature control: air heating and air cooling.
Air Heating:
When heating is required, the HVAC system activates its heating unit, typically utilizing electronic heating elements such as electric heaters, induction coils, or thermostats. The heating element creates a heated zone through which the incoming air passes, warming it before being circulated into the indoor space.
Air Cooling:
To cool the indoor air, the cooling unit is activated. The air is passed through a coil as part of a heat exchanger, which can be of the shell and tube or cross-flow coil type. This heat exchanger contains a refrigerant that absorbs heat from the incoming air, resulting in cooled air. A compressor is responsible for liquefying the refrigerant, facilitating the cooling process.
Air Distribution
After heating or cooling, the treated air is injected into the building using industrial blower fan units, ensuring even distribution throughout the space. This final step is crucial for maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and comfort.
Humidification and Dehumidification
In some cases, HVAC systems incorporate humidification or dehumidification components to control indoor humidity levels. While these processes can be achieved independently of heating or cooling, in dry regions, spray humidifiers may be integrated into HVAC systems to enhance comfort and air quality further.
The Role of Ventilation in HVAC Systems
Ventilation is a core component of HVAC systems and can be categorized as natural or mechanical.
Natural Ventilation: In traditional construction, natural ventilation relies on openings like windows, doors, vents, and other openings to allow air to flow in and out of the building. It replenishes oxygen, removes odors, and helps manage carbon dioxide and moisture levels. However, modern construction emphasizes tight building envelopes, making mechanical ventilation increasingly essential.
Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation, indicated by the ‘V’ in HVAC, utilizes mechanical systems to ensure proper air exchange. It is especially crucial in tightly sealed buildings where natural ventilation is limited. This mechanical process ensures the building receives a steady supply of fresh air.
Conclusion
HVAC systems are pivotal in creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. By regulating temperature, controlling humidity, and filtering the air, these systems enhance air quality and provide year-round comfort. Understanding the working principles of HVAC systems allows for efficient operation and ensures that indoor spaces remain conducive for occupants. Whether in homes, offices, or industrial settings, HVAC systems are an integral part of modern living.