SEER, stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure used to rate how efficiently an air conditioner or heat pump cools a space over a typical cooling season.
Definition of meaning from its formula, a SEER is a ratio obtained by dividing the cooling output of an air conditioner or heat pump over a typical cooling season by the energy it consumes in Watt-Hours.
It’s a score that tells you how much cooling a unit can provide relative to the amount of energy it uses.
SEER2, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2, is an updated version of this calculation. It includes not only the cooling output but also considers the total heat removed from the space during the whole cooling season. The new M1 testing procedure associated with SEER2 is designed to better reflect the real-world conditions in which these systems operate.
The Department of Energy (DOE) made changes to the term “SEER” to “SEER2” to match new regulations starting from January 1, 2023. This adjustment ensures that the rating system keeps up with the latest standards and accurately represents the efficiency of air conditioning and heat pump units in everyday use.
what does SEER mean in HVAC or Air conditioning (AC).
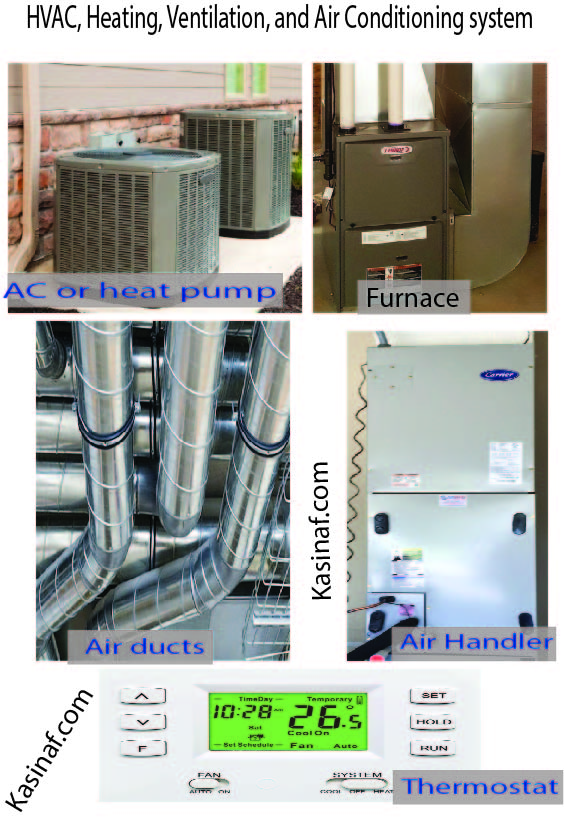
In HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. It’s a measure of how efficiently an air conditioning or heat pump system operates over a typical cooling season. SEER is calculated by dividing the cooling output of the system (in BTUs) by the energy it uses in watt-hours. A higher SEER rating indicates a more energy-efficient system. It helps consumers understand and compare the energy efficiency of different HVAC units when looking for a new one.
Over the past few decades, SEER ratings for air conditioners have gone up a lot. In the 1970s, the average SEER rating was just 6. Nowadays, the minimum is 9.7 for regular ACs and 10 for mini-split systems. If your air conditioner is around 20 years old, it probably has a low SEER rating, meaning it might struggle to cool your home efficiently and uses more energy than newer models.
But if you want to save money, you can find air conditioners with much higher SEER ratings. The best central ACs can have a SEER of 20, and ductless split systems can be even higher. If you replace your old SEER 9 AC with a high-efficiency SEER 18 unit, you could cut your energy use in half.
SEER chart for ac units
Check out the SEER chart: the higher your SEER rating, the less you’ll spend on energy each year. It shows how efficient your HVAC system is. So, spending a bit more on a higher-rated AC unit might save you more money in the long run. This chart also works for heat pump SEER ratings.
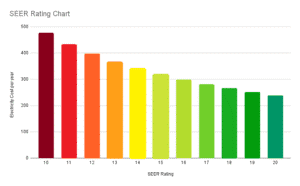
SEER chart for ac units
If you’re considering getting a new system, here’s a chart with SEER ratings and the average cost of an HVAC system. Remember, the prices can vary a lot based on the type, size, brand, SEER rating, and BTUs of the AC unit.
| SEER Rating | Size | Air Conditioning (BTUs) | Average Price* |
| 14 | 3.5 ton | 42,000 | $4,000 |
| 15 | 5 ton | 57,000 | $4,225 |
| 16 | 3 ton | 33,000 | $2,700 |
| 17 | 5 ton | 54,000 | $4,700 |
| 18 | 4 ton | 48,000 | $6,400 |
SEER Rating by Year
| year | Average SEER rating |
| From 2023 | 15 and above |
| 2015 to 2022 | 14 and above |
| 2006 to 2014 | 13 and above |
| 1992 to 2005 | 10 to a2 |
| 1986 to 1991 | 8 and below |
| 1980 to 1985 | 7 and below |
| Before 1980 | 6 and below |
If your air conditioner is old, it probably has a lower SEER rating. But if it’s a newer model, there’s a good chance it’s more energy-efficient. For instance, a 20-year-old AC might have a SEER rating of 10 to 12, while a new one bought this year could have an average SEER rating of 15 or higher.
Benefits of a High SEER Rating
- Saves Money on Energy Bills: A high SEER rating means your AC uses less energy, reducing your cooling costs. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, upgrading to a high SEER-rated air conditioner could save you 20%–40% on cooling energy expenses.
- Reduces Environmental Impact: High-efficiency systems decrease reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. Newer models also use safer, ozone-friendly refrigerants, contributing to a greener environment.
- Eligible for Incentives and Rebates: Many states offer rebates for high SEER-rated HVAC units. Energy Star-certified AC units qualify for a $600 tax credit from Jan. 1, 2023, to Dec. 31, 2032. Check the Energy Star Rebate Finder for local offers.
- Efficient Moisture Removal: High SEER systems remove moisture more effectively, preventing mold and enhancing indoor air quality. This is especially beneficial for those with allergies or respiratory conditions.
Upgrading to a high SEER-rated air conditioner brings cost savings, environmental benefits, and potential incentives, making it a wise investment for your home.
Making Your AC More Efficient. SEER rating optimization
Each air conditioner comes with a suggested AC SEER rating from the maker. But since every home is different, your actual energy performance can be different. Factors like the local weather, how your home is set up, the quality of ducts, and insulation can make your efficiency higher or lower than what the unit is rated for.
how to find SEER on ac unit?
To find your AC SEER rating, look for a black and yellow sticker or label on the side or back of your cooling system. The big numbers on that sticker will show your SEER rating.
what is the best SEER rating for ac 2024?
For those watching their energy bills, it’s smart to pick an air conditioner with a higher SEER rating. A SEER of 18 or more is considered excellent for efficiency and cost savings. Remember, higher ratings usually mean higher costs, so budget wisely when choosing a new AC. Also, consider factors like size, installation, and maintenance. Look for units with certifications like ENERGY STAR® for reliable, cost-
effective cooling.
How to increase your ac Energy efficacy with out buying new air-conditioning system (AC)
To boost your home’s energy efficiency without getting a new AC, consider adding insulation, sealing ducts, and placing the outdoor HVAC unit in the shade. These steps can improve HVAC efficiency ratings. We’re here to help you optimize your home for efficient cooling.
is a higher SEER rating better
Yes, a higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is generally better when it comes to air conditioners. A higher SEER rating indicates greater energy efficiency, meaning the system can cool your space using less electricity. This can lead to lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact.
if you compare a 10 SEER AC to a 20 SEER system, the 20 SEER system is twice as efficient. That mean if you use a 10 SEER AC unit to cool your home you will need twice the energy used by a 20 SEER to cool the same space.
However, it’s important to balance the benefits of a higher SEER rating with the upfront cost of the system. It’s recommended to consider factors like your budget, local climate, and long-term energy savings when choosing the SEER rating for your air conditioner.
Performance measures for heat pumps and AC units:
Coefficient of Performance (COP):
This is the ratio of the heat pump’s output power to its input power. A higher COP signifies greater efficiency in both heating and cooling modes.
COP=Input Power/Output Power
COP is a dimensionless number, representing the efficiency of the heat pump. A higher COP indicates better efficiency in both heating and cooling.
Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER):
EER is the ratio of output cooling energy (in BTUs) to electrical input energy (in Watt-hours). It measures cooling efficiency over time.
EER=Input Electrical Energy (Wh)/ Output Cooling Energy (BTUs)
EER measures cooling efficiency over time, with units in BTU/Wh.
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER):
SEER is the ratio of output cooling energy to electrical input energy, measured over a season with varying outdoor temperatures. A higher SEER indicates better overall efficiency in cooling.
SEER=Input Electrical Energy over the Same Season (Wh)/Output Cooling Energy over a Season (BTUs)
SEER reflects how well the system performs over a season with varying outdoor temperatures.
Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF):
Similar to SEER, HSPF measures efficiency, but specifically in heating mode. It uses the same units as SEER and provides insight into the system’s heating efficiency over a season.
HSPF=Input Electrical Energy over the Same Season (Wh)/ Output Heating Energy over a Season (BTUs)
HSPF measures the efficiency of the system in heating mode over a season, using the same units as SEER.
how seer is calculated
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is calculated using a formula that involves measuring the cooling output of an air conditioner or heat pump over a typical cooling season and dividing it by the energy consumption in watt-hours during that same period. The formula is as follows:
SEER=Total Cooling Output (in BTUs) / Total Energy Consumption (in Watt-Hours)
SEER takes into account the efficiency of the system under different outdoor temperatures and provides a standardized measure of the cooling efficiency over an entire season. A higher SEER rating indicates a more energy-efficient system. Keep in mind that SEER is a ratio and is dimensionless.
What is the Difference Between SEER and SEER2?
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and its updated version, SEER2, are measures used to evaluate the efficiency of air conditioning systems. SEER represents the ratio of cooling output to energy consumption over a typical cooling season, offering a standardized way to gauge efficiency. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficiently the air conditioner operates. However, SEER has limitations, as it provides a maximum efficiency rating under specific conditions, and real-world performance can vary.
SEER2 introduces improvements in testing conditions to better align with typical residential scenarios. The key modification involves raising the total external static pressure testing conditions, making them more reflective of the challenges faced by ducted systems in regular homes. This adjustment addresses concerns that SEER testing conditions didn’t adequately consider the impact of ductwork on external static pressure, leading to potentially inaccurate efficiency assessments.
In essence, SEER2 aims to provide a more accurate representation of a system’s efficiency by refining testing conditions. Both SEER and SEER2 are crucial for consumers seeking energy-efficient air conditioning solutions. Understanding these ratings helps individuals make informed decisions, balancing factors like upfront costs and long-term energy savings while contributing to overall efforts to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Efficiency ratings can be tricky, especially with recent DOE changes. Let’s break down SEER and SEER2 to clear up the confusion.
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio):
SEER is a measure of how well an air conditioner cools over a typical season. It compares the cooling output to the energy used in watt-hours. Think of it like miles per gallon for your car – the higher the SEER, the more efficiently your AC works. However, this is a maximum efficiency rating, and real-world conditions can make it lower.
SEER2 (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2):
The main difference is in the testing conditions. DOE raised the testing conditions for SEER2 to better reflect real-world scenarios in typical homes. The change addresses issues with SEER testing not accounting properly for the influence of ductwork on external static pressure. By aligning SEER2 more closely with actual conditions, it aims to provide a more accurate representation of a system’s efficiency.
Top of Form
















