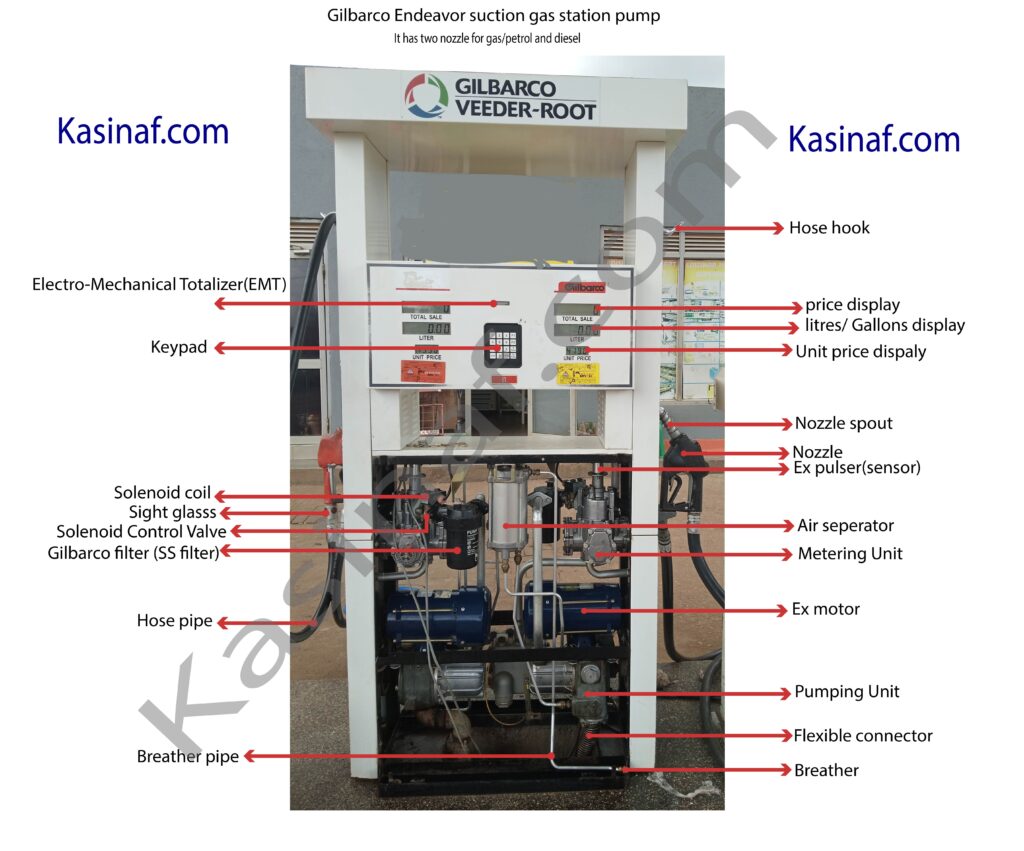
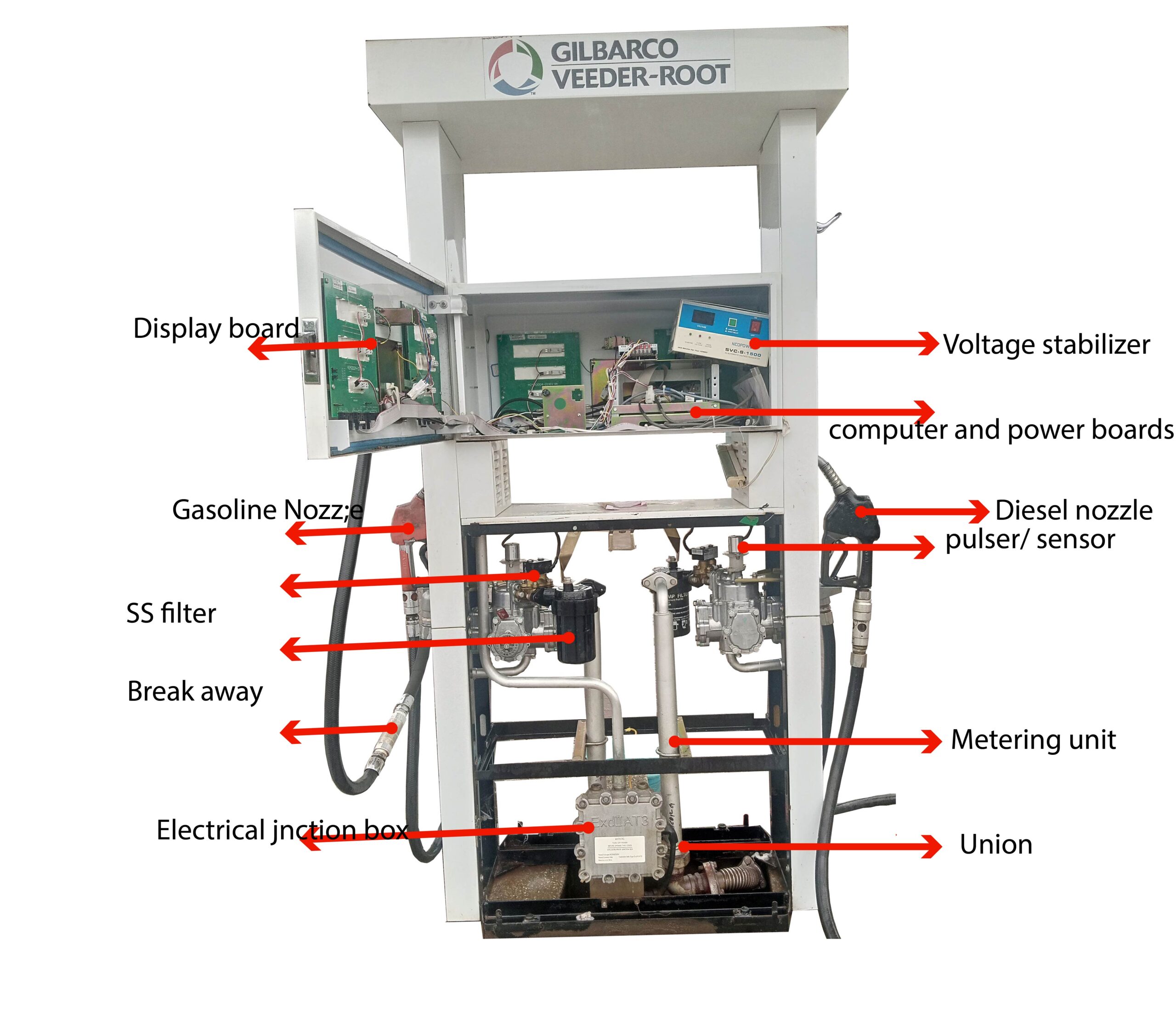
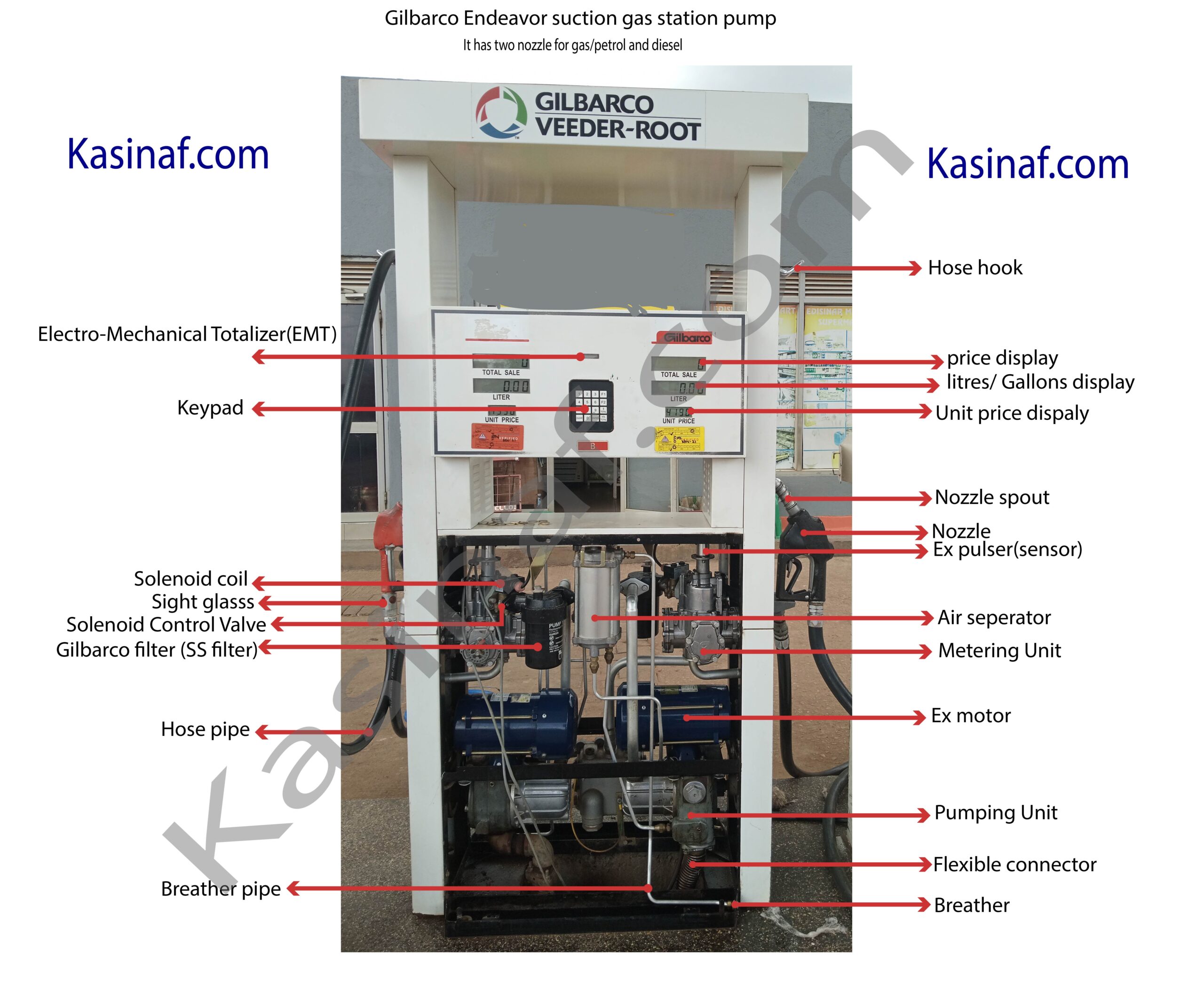
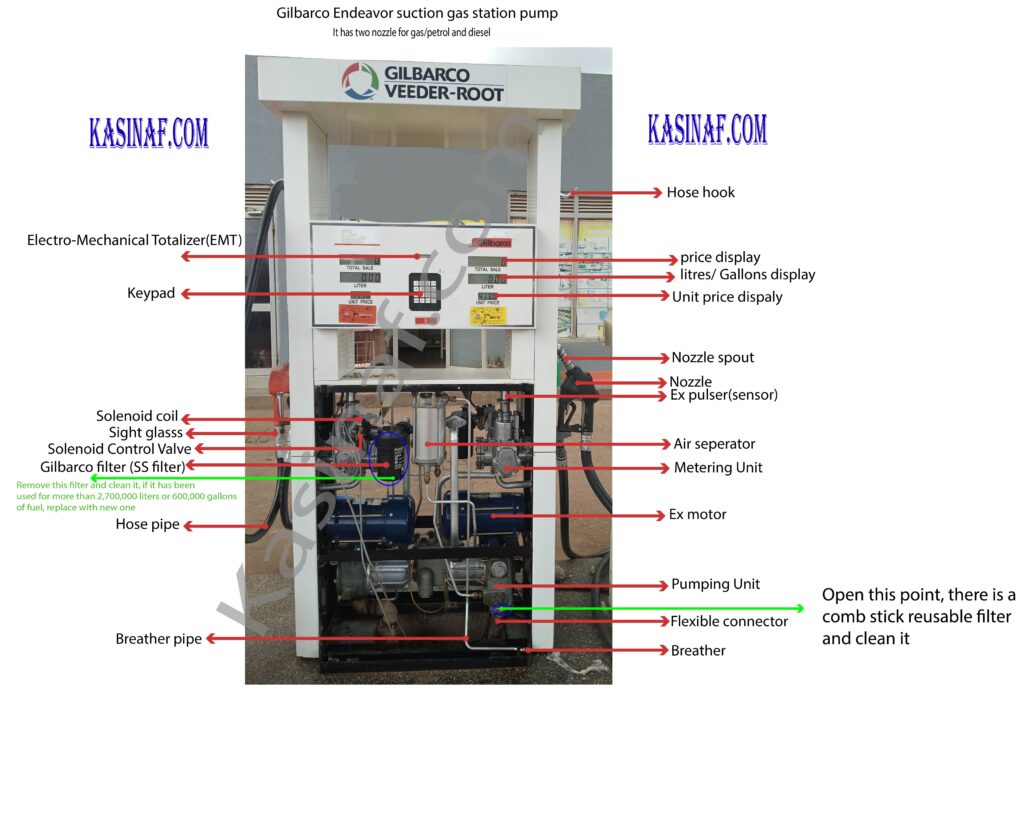
Fuel dispensers at gas stations are equipped with several safety features to prevent fuel leaks and fires, especially in the event of a collision or impact. One critical component in this safety mechanism is the shear valve. This article aims to demystify shear valves, explaining their importance, how they work, and the key considerations for their proper installation and maintenance.
What Are Shear Valves?
Shear valves are a critical safety component found in fuel dispensing systems, designed to minimize the risk of fuel leakage or pouring in the event of a vehicle colliding or knocking a fuel dispenser .
Their primary role is to prevent fuel release if a dispenser is hit by a vehicle. According to regulations, shear valves are mandatory for all pressurized piping lines, with suction systems being the only exception.
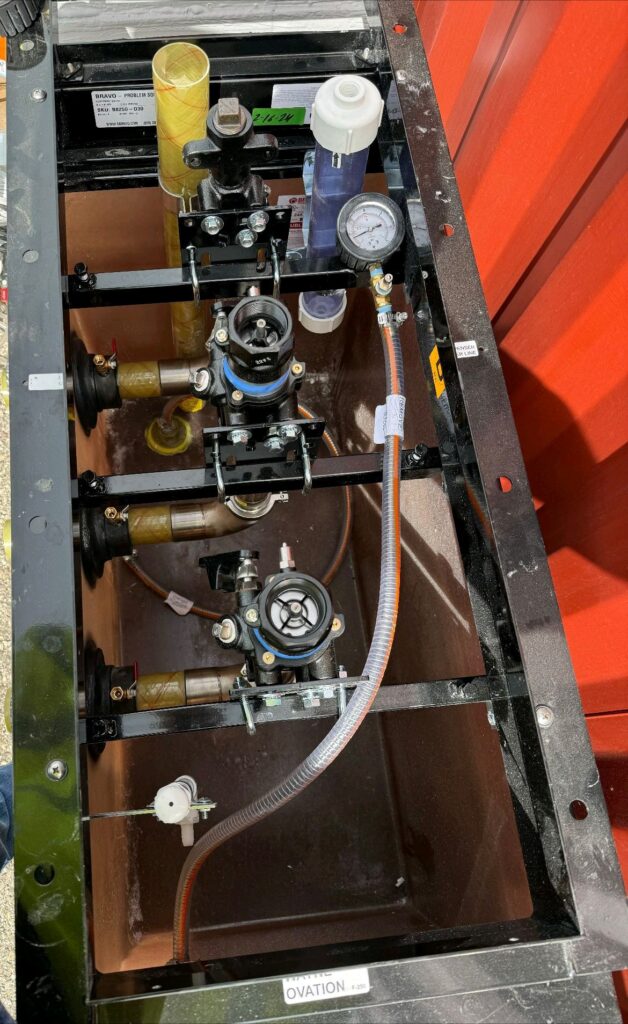
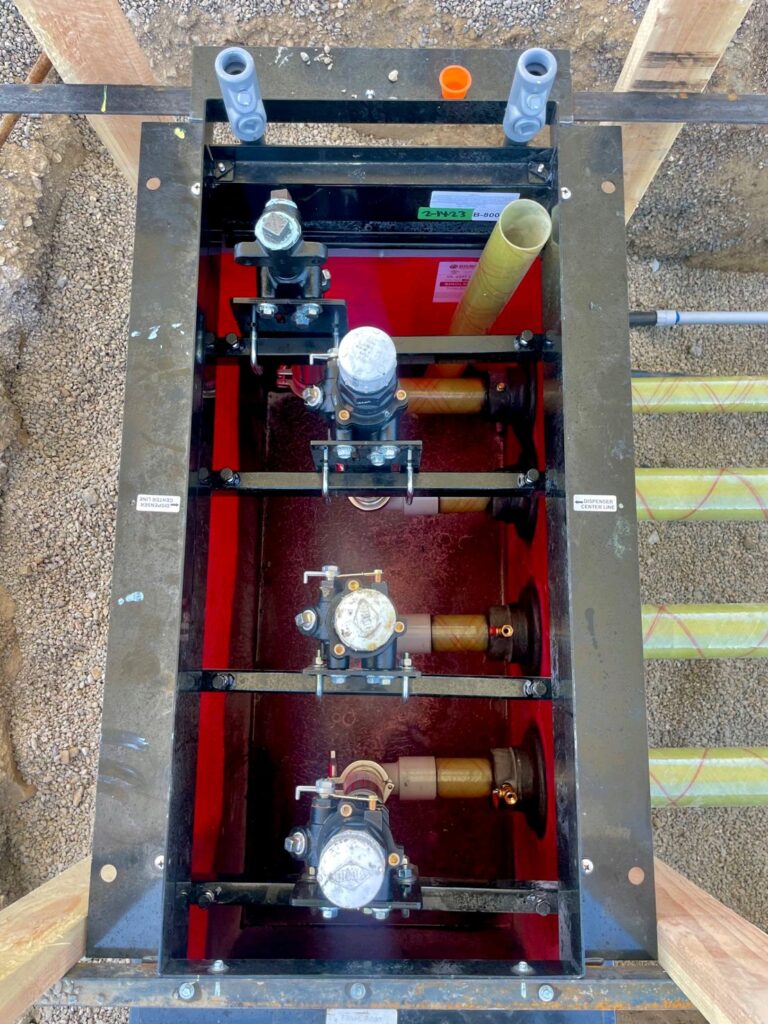
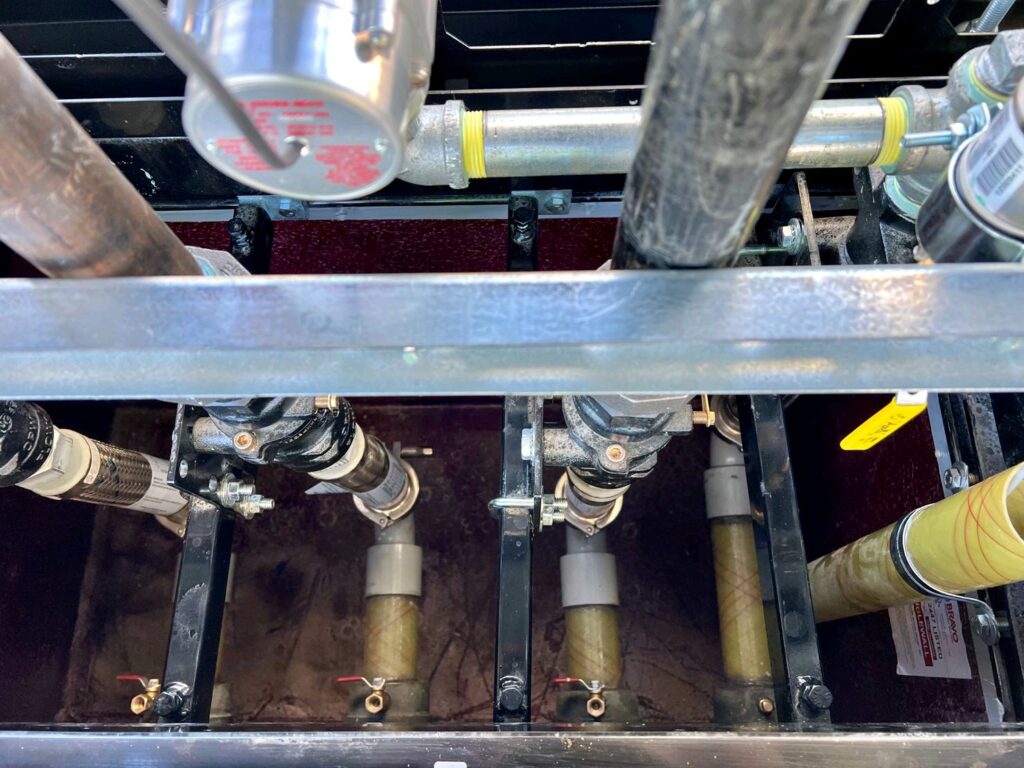
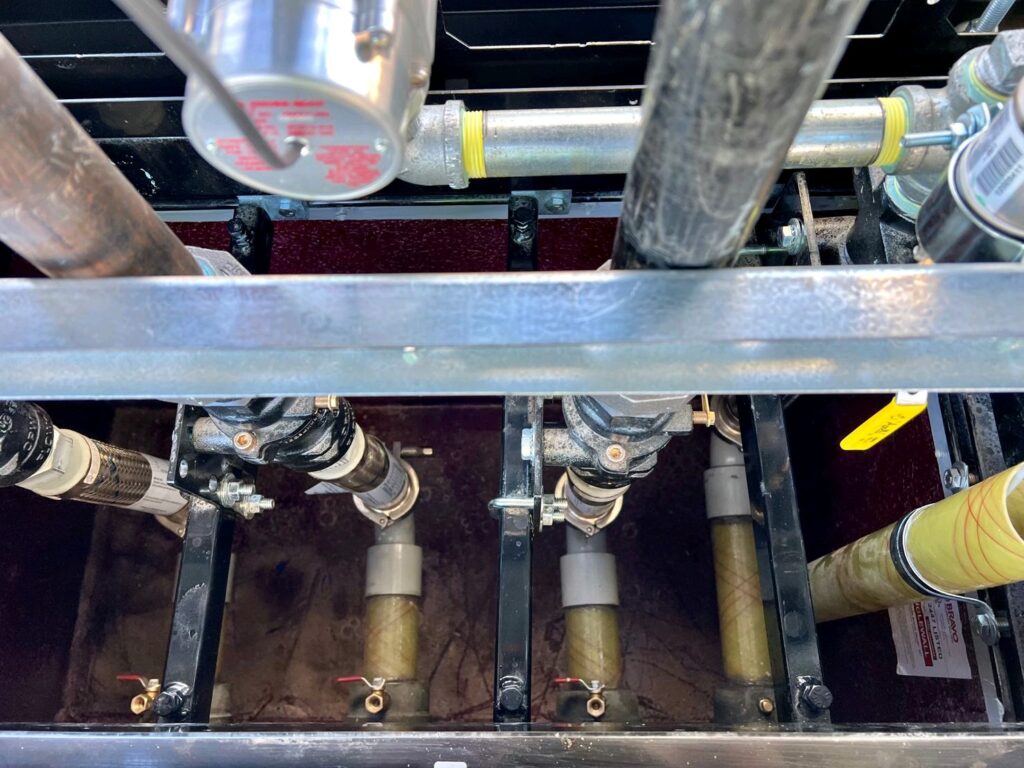
A shear valve consists of a valve mechanism that is spring-loaded, designed to snap shut in the event of significant impact. It features a shear point engineered to break under force, effectively sealing off the fuel flow and preventing leaks.
How Do Shear Valves Work?
Shear valves are a critical safety component found in fuel dispensing systems, designed to minimize the risk of fuel leakage or pouring in the event of a vehicle colliding or knocking a fuel dispenser . Their operation is relatively straightforward but ingenious, combining mechanical principles with robust design to protect both property and lives. Here’s a simple breakdown of how shear valves work:
Basic Components
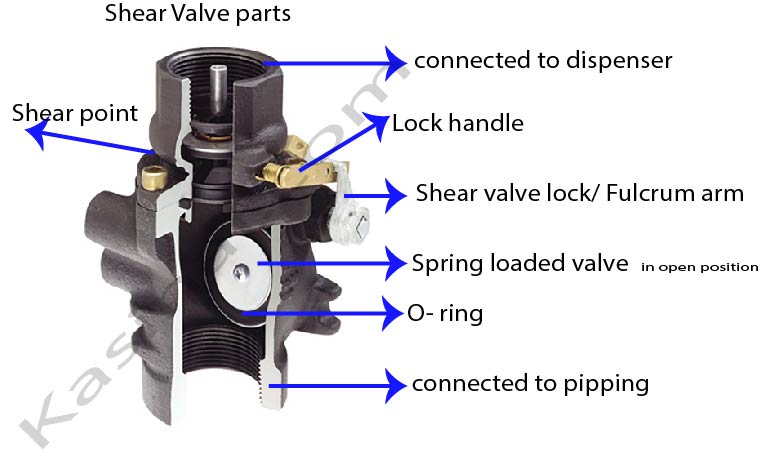
- Valve Mechanism: This is the part of the shear valve that controls the flow of fuel. It is usually spring-loaded, meaning it is kept open by a spring mechanism under normal conditions to allow fuel to pass through.
- Shear Point: A predefined weak spot in the valve designed to break or shear off when subjected to a significant force or impact.
- Fulcrum Arm: A part of the valve that plays a crucial role in its operation, ensuring the valve snaps shut when the shear point breaks.
Operation in Normal Conditions
Under normal operating conditions, the shear valve remains open, allowing fuel to flow from the storage tank to the dispenser for fueling vehicles. The spring-loaded valve mechanism is calibrated to stay open against the pressure of the fuel flowing through it.
Operation during an Impact
- Impact Detection: When a vehicle collides with a fuel dispenser, the force of the impact is transferred to the shear valve. If the force exceeds a certain threshold, it triggers the shear mechanism.
- Activation of the Shear Point: The designed shear point on the valve is the weakest part of its structure. This point is engineered to break under a specific amount of force, which is what happens upon impact. The breaking of the shear point is a critical step, as it initiates the safety shutdown process.
- Closure of the Valve: Once the shear point breaks, the spring-loaded valve mechanism is activated to snap shut. This action is facilitated by the fulcrum arm, which ensures the valve closes quickly and securely. The sudden closure of the valve stops the flow of fuel almost instantly.
- Isolation of Fuel Supply: By snapping shut, the valve effectively isolates the fuel supply. This means that even though the dispenser may be damaged or dislodged from its position, the fuel line itself is sealed off at the point of the shear valve. This greatly reduces the risk of fuel leakage, which in turn minimizes the potential for fire or environmental contamination.
Ensuring Proper Function
For a shear valve to function correctly during an impact, it must be properly installed and anchored. This includes ensuring all bolts are tight, the valve is securely attached to the stabilizer bar, and that the stabilizer bar is firmly anchored. Incorrect installation can prevent the valve from operating as intended during an emergency, leading to potential fuel leaks and other hazards.
Installation and Anchoring
The effectiveness of a shear valve heavily relies on its correct installation and anchoring. Here are key points to ensure a shear valve functions as intended:
- Proper Anchoring: Shear valves must be securely anchored to withstand impacts. This includes tight bolting and firm placement against the stabilizer bar, which itself should be rigidly anchored to the dispenser’s side walls.
- Avoiding Installation Errors: Examples of poor installation include missing stabilizer bars, loose or missing bolts, and gaps between the valve and stabilizer bar or face plate. Such mistakes compromise the shear valve’s ability to function correctly under stress.
- Ensuring Full Movement: The fulcrum arm, a part of the shear valve, must have enough clearance to rotate fully. If it cannot, the valve may not close properly, risking fuel release.
- Use of Correct Components: Depending on the design, shear valves may require specific components like U-bolts or channel irons for correct anchoring. These components must be installed as per the manufacturer’s specifications.
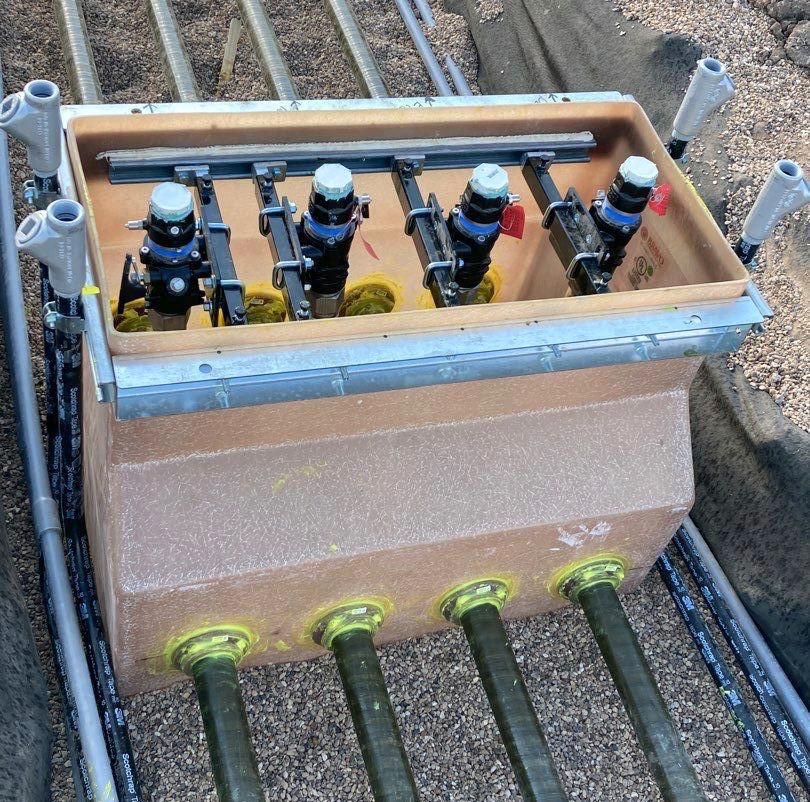





The Consequences of Improper Installation
Improperly installed shear valves can lead to catastrophic outcomes. In minor incidents, the stabilizer bar may separate, reducing the valve’s effectiveness. In more severe cases, such as when a dispenser is knocked over without the shear valve activating, the consequences can include significant fuel leaks and fires. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to prevent such outcomes.
Conclusion
Shear valves play a vital role in the safety of fuel dispensing systems, designed to prevent fuel leaks during accidents. Their effectiveness, however, is highly dependent on proper installation and maintenance. Adhering to industry standards and manufacturer specifications is non-negotiable to ensure these devices perform their critical safety functions when most needed. Gas station operators and maintenance personnel must prioritize the correct installation, regular inspection, and maintenance of shear valves to safeguard against potential hazards effectively.
shear valves for sale and its spares: spatco.com shear valves
Shear valves from OPW : OPW shear valves
links
https://scdhec.gov/sites/default/files/docs/Apps/Environment/USTOperatorTraining/Content/Lessons/Shear%20Valves.pdf